Deep plane face & necklift
Droopy facial features, pronounced nasolabial fold, double chin and loose skin on the neck are common aesthetic problems that occur both in men and women. Most plastic surgeons use face and necklift procedure to rejuvenate the aging facial features . However, if the procedure is performed only superficially, the result will only last for a limited time and after a while a recurrence will occur – the tissues become loose again and drop. Therefore, in most cases, I choose the deep plane technique for my patients – an advanced technique that focuses on correcting the deep structures of the face and neck.
Deep plane face & necklift
What is deep plane face & necklift
By the deep plane technique, we mean an operation in which the surgeon focuses mainly on the deep structures (deep plane = deep layer), which are located within or under the SMAS (Superficial Musculoaponeurotic System) layer of the face.
Why we go deep? Why not only lift the skin and go home? Well, the skin is just a cover and most of the aging processes take place within the structures, that are underneath. The skin only reflects what is happening in the deep. Indeed, the skin may be damaged also superficially by sun exposure and atrophy, but when it is sagging, bulging, becoming loose, that all happens due to the problem in the deeper layers. This applies on the face as well as the neck.
In the neck area, there is another issue. It is the accumulation of volume resulting in a double chin, which is aesthetically unpleasant. It is caused by subcutaneous fat layer accumulation, but the main problems occur again in the deep layer under the platysma muscle located more deep under the skin. The problems include also tissue loosening and sagging and submandibular salivary glands descend.
At the same time, as we age, the bone support of the chin undergoes atrophy, and the tissues that were originally hidden by the bony shell of the lower jaw do not fit in and become visible under the chin.
Each person is individual, and the final solution of the problem is evaluated by the surgeon during the consultation and operation according to what he or she finds.
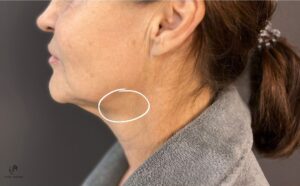 Fig.: Droopy face and neck tissues with visible submandibular salivary gland before surgery
Fig.: Droopy face and neck tissues with visible submandibular salivary gland before surgery
Why deep plane facelift?
There are many types of facelifts out there – skin only lift or minilift, SMAS plication, imbrication, SMAS lift, deep plane lift, etc. Why I prefer deep plane facelift technique?
In my work, I always try to achieve the best possible result to meet the expectations of the patient and to provide the most durable effects. This applies to face and necklift procedure the most. Independent on the technique, the patients always look great during the first few months. Why? Because they are swallen. The swelling lasts for about 3 months and then goes. And only then we see the real result. This is disappointing because we want the perfect look to stay. Depending on the technique used, the result can only be evaluated properly after this period ends.
Since I have done all of the facelift techniques that were described, I found that some of them are not that powerful and effective in the long term. This leads to disappointment of the patient as well as the surgeon. Procedures like minilift and techniques with limited dissection of tissues fail the most and also result in deformities.
The deep plane technique is different. With this procedure, I do not dissect skin from the deeper structures too much, since it is not needed. I rather dive into deep, release the deeper structure fixation points in a natural so called gliding plane, which is rather avascular (contrary to the plane under the skin which bleeds a lot) and by releasing the fixation points in the deep, I can achieve very smooth lift without tension. The tissues glide freely, they don’t bleed and that is all what we want.
Fixation points in the deep plane
There are several, anatomically defined areas that fix the deeper SMAS tissues to the bones of the face. These are zygomaticofacial ligaments, masseteric ligaments, mangibular ligaments and cervical retaining ligaments. If these adherent areas are not completely released, the tissues don’t glide on each other. Without release, the lift only pulls on these fixation structures, which causes pain and after swelling goes, they return back to their original position. So really we have to release them to achieve a long lasting result.
Another important reason for this maneuver is tension. The fixation points and their importance is well described above. We want no tension on any fixation points. Now the tension on the opposite side, near the ear, where the scars are located, is also wrong and causes further issues. Tension in general is wrong in case of a facelift. With the lift after full release of fixation points, we don’t need to apply any tension on the incision area around the ear and all the tissues are just simply repositioned and laid to the new position including skin, which is loosely sutured. This is great advantage, because scars under tension lead to hypertrophy and migration and also the earlobe is pulled by tension to aesthetically unpleasant pixie ear deformity.
These are the reasons I don’t like tension in my lift and the only option to avoid it is the deep plane technique.
„So please don’t ask me for a minilift, I won’t do that and no other technique. I want the best possible result for you and this cannot be achieved with no other technique than a deep plane technique.“
Why deep plane necklift?
It has been shown that the removal of the double chin, for example by liposuction alone or other less invasive techniques may not be completely successful in achieving the desired jaw contour, especially because the deepest deposits of fat stored under the platysma muscle are not repositioned at all and any other problem structures are not treated.
Also, simply lifting the neck structures during a simpler necklift often fails in the long term.
„It’s similar to trying to shrink a beer belly with belted pants. Likewise, the neck and chin cannot be reduced by shrinking the neck structures. The belly band, as well as the neck structures, will eventually loosen and return to their original state. However, if the belly looses weight, we can pull it down easily with a belt. The same applies to neck surgery. Belly slimming is the equivalent of an operation in the depth of the neck – a deep plane necklift.“
MUDr. Radek Lhotský
This is a technique intended for experienced surgeons who know very well the anatomical area and the operative techniques of facial aesthetic surgery. The great advantage of this advanced technique is the durability of the result, which is not affected by significant weight changes in the future. Therefore, recently many patients prefer to choose the deep plane technique.
The essence of the operation is therefore the removal of any excess tissues in the neck area in order to achieve the best possible contour of the transition between the jaw and the neck, and thus the youthful and fresh appearance of this area. This mainly involves the removal of excessive accumulation of fat between the muscles in the chin area, reduction of the submandibular salivary gland, or the reduction of excess muscle that forms the floor of the oral cavity, and other advanced operative maneuvers. At the same time, the fat deposits under the skin in the subcutaneous area (where there is not much fat usually) are conservatively removed, and finally the muscle of the superficial layer of the neck – the platysma – is lifted and tightened. During the procedure, the skin in younger patients shapes itself into a new contour, or in case of a larger excess, it is removed through an additional incision behind the auricle (extended necklift).
The operation can be performed alone, especially in younger patients who do not yet have droopy face area, or it can be combined with a deep plane facelifting, i.e. a complete face and necklift.
Additional maneuvers to deep plane face & necklift
Submandibular salivary gland
An interesting and very effective part of the deep plane necklift is the partial resection of the submandibular salivary gland. This gland is one of many glands that produce saliva. Its size affects the fullness of the submental area and causes a lack of the sharp neck contour. In fuller necks, the gland can be identified by palpation as a larger or smaller lump of about 1.5 cm in size, which is accentuated by pressure of the tongue against the palate; in thinner necks, it is visible from the side.
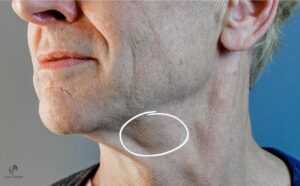
Fig.: Protruding submandibular salivary gland before resection
In about a third of patients who come for neck surgery, it is appropriate to partially reduce the size of the gland. We reduce the superficial lobe of the gland, most of the gland then remains in the depth of the floor of the oral cavity and its function is preserved. Mendelson et al. in a sample of 112 patients demonstrated no risk of insufficient saliva production after superficial lobe removal (1). The main risks include mainly acute bleeding in the early postoperative period and the risk of a salivary fistula from leaking saliva into the surgical area. At the same time, there is a higher risk of temporary disruption of the innervation to the lower lip, due to the proximity of one of the branches of the facial nerve on the outer side of the gland capsule. However, these risks are small. We perform the resection using special Ligasure equipment that is used for surgery of other glands in the body, for example the pancreas, thyroid gland, etc., which requires relatively expensive consumables. Therefore, the price of this additional procedure is added to the base procedure for patients who require it. The result without the reduction of the gland will never be as good as it could be.Also, Ligasure device provides better control over postoperative and peroperative bleeding and reduces the risk of saliva leak to a minimum.

Fig.: Ligasure Exact device used for reduction of the submandibular salivary gland
„In order to regain a firm, sharp and defined jawline of the neck, it is mandatory to release the fixation points of the tissues on the face and neck and move the middle drooping mobile part upwards and backwards and other maneuvers on the neck. These maneuvers are performed in the deep layer of the face, as part of the deep plane face and necklift method. Only then is it possible to achieve a perfect jawline as we see in the illustration.“ MUDr. Radek Lhotský
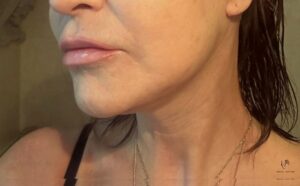
Fig.: Perfect jawline after deep plane facelift and necklift
Diet is an essential part of aftercare after salivary gland resection. The aim is to limit the stimulation of the salivary gland in order to avoid the production of saliva in the neck area with the need for subsequent drainage. Diet after salivary gland trimming may be found here.
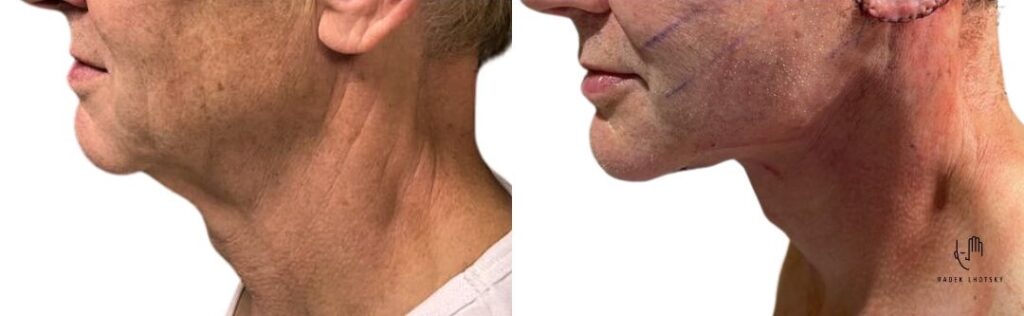
Fig.: Comparison of the situation before submandibular gland reduction and after its trimming during a deep necklift procedure
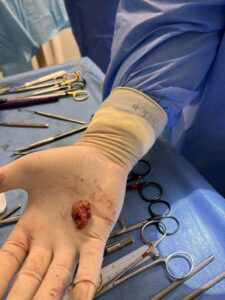
Fig.: Removed submandibular salivary gland within a deep necklift procedure
Why is chin liposuction unsuitable minimally invasive alternative to deep necklift?
Liposuction in its principle focuses on fat layers stored under the skin. This fat layer on the neck is very thin in most people, about 0.5 cm in diameter. Only in very obese patients it reaches larger volumes. The fat layer in the subcutaneous tissue is also responsible for the youthful appearance of the skin, hydration and tightened appearance. If we remove this very thin layer with liposuction, scarring of the skin to the muscle occurs, unevenness occurs and the skin loses its nice, tight appearance. That’s why I only minimally recommend liposuction and rather use it as an additional maneuver as part of a necklift if the layers of fat are excessive. The idea that we can smooth out the unsharp contours of the neck with liposuction is completely wrong and the procedure can lead to dissatisfaction and frustration since the desired result is not achieved.
Earlobes
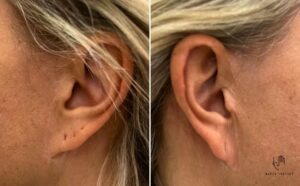
In the elderly people, it is possible to see that the earlobes lengthen and atrophy. It is a natural process, atrophy occurs everywhere on the body. Sometimes more, sometimes less. As a part of the procedure in this area (either the necklift itself or rather as a part of the deep plane facelift), it is really possible to perform the correction of the lobes as well. We treat atrophy by applying a small amount of patient’s own fat, and the lengthening by partial resection of the lobe.
If the patient has already had facelift surgery in the past, we frequently encounter the so-called pixie ear deformity as shown on this image:
Fig.: Pixie ear deformity of the earlobes
It is a deformity that is caused by excessive tension on the skin, when the subcutaneous SMAS layer was not sufficiently released and fixed, and the surgeon concentrated all the lifting pull just to the skin. It is bad. The lobule cannot withstand the pull and stretches and the scar migrates and is visible as on the image above. In the deep plane technique, all the forces that could act on the lobule are concentrated on the deep tissues, and the skin is only loosely placed and stitched to the lobule, so that no forces could act on it.
Here is another big advantage of the deep plane technique, and it basically applies to all the skin that is loose during the face and necklift. There is no traction on any part of the scar nor lobule. Therefore, the scars are very thin and do not migrate.
The correction of this deformity involves a complete redesign of the lifting operation in the deep plane, release of the fixation and anchoring of the deep structures properly and replacing the skin without tension on the suture. Simple excision of the scar does not solve this problem because the traction will re-engage and the lobule will pull out again and scare will stretch and migrate to become visible.
Revision surgery after a previous lift
In the past, there were exclusively used such lifting operations that performed the lift only within the skin or surface layers. These include e.g. SMAS plication or resection or its repositioning, without release of the fibrous attachments in the deep layer. This meant that the effects were not and could not be durable and perfect. I have even come across the opinion of renowned experts in the field who still claim that there is no need to do anything with the neck. That is wrong. A well-contoured neck is essential for overall facial rejuvenation. Therefore, I consider the deep necklift technique to be one of the most important for achieving significant rejuvenation.
There is a partial advantage of the deep plane technique in the case of previous surgeries. In principle, we say that where the previous operation with dissection ends, the deep plane just beggins. During the revision, we often skip over the previously operated terrain and get to the still virgin tissue. This also proves that the effect is completely different. However, the problem with revision procedures is the excessive amount of previously removed skin, pulled lobes and overall scaring of tissues (for example, after previously performed liposuction of the neck, etc.). We often do not know what we will actually encounter during the revision and how the operation will be performed. That is why revision surgery tends to be more demanding, longer and, unfortunately, more expensive. Sometimes the repair of a previously performed lifting is not completely possible and it is necessary to take this into account.
Fillers, lifting threads and facelifting
The situation during our surgery is further aggravated by repeatedly applied fillers. Filling materials can be absorbable or non-absorbable. Both of these materials induce changes in the tissues, persist even longer than the manufacturer declares, and generally worsen the quality of the tissue where the operation takes place. If you regularly inject fillers or lifting threads, prepare for problems, especially longer-lasting swelling and poorer healing, which may or may not affect the result. If possible, and if you are considering a facelift in the future, avoid using these substances and materials, or have them dissolved beforehand.
Fatgrafting in facelifting
My favorite addition to a facelift or necklift is fat grafting – the transfer of one’s own fat tissue to the face area.
Fat is a very interesting material that comes from the body’s own fat deposits. The harvesting is carried out at the beginning of the surgery and after processing it is injected to the planned locations. Fat has many effects, one of them is the addition of missing volume, another is the correction of various irregularities, wrinkles or shadows, but also, for example, a change in the skin color in areas where the muscles or deeper structures became visible through the skin and cause shadows and discolorations.
An interesting form of specially processed fat is the so-called nanofatgraft. It is fat that has been stripped of fat cells, so it is not actually fat. This material is significant in that the fat cells are destroyed and it only contains mesenchymal stem cells. These cells are in a resting state, but after the destruction of the surrounding fat cells, they are activated in order to repair damage. It is a simplified principle of the mechanism, however, the activation of stem cells is to start the process of repair and regeneration. It is strange that regeneration does not only take place in the sense of repairing destroyed fat cells, but also restoration and repair of other damaged tissues. Using nanofatgraft, it is then possible to solve atrophy and tissue damage due to aging, regenerate the skin, improve hypertrophic or atrophic scars, improve hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation and many other effects. During a facelift or necklift, I use it to improve the skin, hydrate and improve the quality of the lips, overall improvement of the SMAS layer, which is responsible for the quality of the skin attached to it, and a lot of other possibilities.
Although the exact mechanism of action of nanofat grafting is not yet known, the effects are widely published and the results of individual applications are freely available. (3) (5) (6) Another possibility of using nanofat grafting is to mix it with your own plasma to further improve the effect. (4)
Detailed consultation is required before surgery
Deep plane face and necklift is a complex operation that we perform under general anesthesia, and the preparation for the operation also corresponds to that. If you are considering rejuvenation through a deep plane technique, we will first meet for a consultation, during which you will tell me your expectations and the goal of the operation. Through the examination, I will determine the degree of loosening of the tissues, the elasticity of skin and possibly the amount of accumulated fat, and we will evaluate the size of the submandibular gland.
The consultation can also be done online. But for that I need precise illustrative photos. You can read how to take photos for an online consultation here.
If it turns out that you are a suitable candidate for a deep plane technique and you are familiar with the risks to which you will agree, we will arrange a date of the operation. You will receive all pre-operative instructions and a list of examinations that must be completed before the operation (most of them, however, can be done at the Prague clinic on site when you arrive).
The most important precautions before surgery include:
– reduce or preferably completely avoid smoking at least 2-3 weeks before surgery – smoking has a negative effect on wound healing
– stop or modify the use of blood-thinning drugs (e.g. Acylpyrine, Alnagon, Anopyrin, Godasal, Aspirin, Mironal or Warfarin, but also any herbal nutritional supplements that sometimes worsen blood clotting)
– pre-operative examination including ECG, laboratory tests (blood count, basic biochemical examination, bleeding and coagulation, laboratory tests for sexually transmitted diseases – HIV, syphilis and liver diseases – jaundice)
Course of surgery
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia. It is not possible to perform some maneuvers under local anesthesia due to intolerance of the pain they can cause. Also for the comfort of the patient and surgeon and safe control over the airways by the anaesthetist, it is better to put the patient to full sleep. The surgery lasts long so it may be a bit uncomfortable for the patient to lie on the operating table for a long time.
The incisions are placed in front of the side burn, in front of the ear, behind the ear and along the hairline at the back. In case of a necklift, there is an additional incision of around 4 cm in length, which is hidden under the chin.
The dissection is accomplished partly under skin, just about 3-4 cm and than I dive to the deep plane to release the fixation points. On the neck I also dissect the individual layers of tissues – fat, muscles and platysma, salivary gland, … and stitch the platysma muscles together for chin support.
After performing all operative maneuvers, we remove any excessive skin around the ear and carefully close the wound with several non-absorbable stitches.
The newest technique for improving the quality of the skin of the neck as part of a deep necklift is to leave a part of the skin and the platysma muscle on the neck connected without mutual separation – the preservation necklift technique. This does not disturb the blood circulation of the skin, and its quality, and by tightening the underlying muscle, the skin is simultaneously smoothed, lifted and significantly improved in appearance. The same happens also on the face, where most of the skin that was dissected from the SMAS layer is actually removed and remains only little strip of skin detached around and behind the ear. The rest of dissection is deep.
This is only possible with the deep plane technique, because the lifting maneuver takes place under the SMAS layer (deep layer), not under the skin as with all other facelift techniques used – in this it is unique and achieves significantly better results.
Possible complications of deep plane necklift
The main risk of this operation is bleeding in the early postoperative period. It is more common when a lot of dissection is taking place under the skin (not the case of deep plane and especially of its preservation variant). In case the procedure involves treatment of the submandibular gland, there is a small risk of fluid accumulation in the neck area during saliva production. This needs drainage.
Patients often experience numbness of the skin that was lifted, but this resolves on its own after few months.
Another problem is wound healing, hypertrofic scaring and dehiscence and migration of scars and earlobe, as discussed above. The advantage of deep plane technique being almost tension free is, that wound healing is undisturbed and risk of migration and pixie ear deformity is very low.
Risk of nerve damage to the facial nerve during deep plane facelift
More invasive sub-SMAS facelift procedures such as the deep plane and composite techniques are often the subject of much criticism by patients and surgeons alike who feel that because of the anatomic plane of dissection the procedure will carry a higher risk of nerve complications; however, this is not corroborated by a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis performed by A. Jacono in 2019 in a metaanalysis of 183 studies that fulfilled the eligibility criteria for comparison. (7)
According to this study, temporary nerve dysfunction (neurapraxia) is ocurring in around 0,69% of cases as opposed e.g. to 1,85% of cases in high lateral SMAS lift and is similar to the less invasive SMAS plication techniques (0,69%).
Permanent facial nerve injury was reported in SMAS flap (0.04%, n = 14,253) and high lateral SMAS (0.08%, n = 1300). No permanent facial nerve injuries were reported for composite (n = 727), deep plane (n = 1795), SMAS imbrication (n = 3254), and SMAS plication (n = 5638). There was no statistically significant difference in overall incidence of permanent facial nerve injury comparing all techniques (P = 0.99).
So this shows, that the dissection plane used to carry out the deep plane facelift is very safe and comparable to all other techniques. As for the deep plane necklift, the risk of damage to the nerves that occur in the vicinity is also very small, mainly because the important nerves are located rather outside the immediate operative field.
The most common problem that we encounter in the deep neck is a temporary lower lip motility disorder, which is manifested by the dysfunction of the lip depressor muscle and a temporary deformity. This is the result of manipulation in the deep layer, not always a nerve injury as such but also injury to the platysma muscle, that contributes to the function of the lips.
So the lip disorder may have many causes and the localization of the damage site is not always precisely possible, however, the disorder is reversible and the function recovers within the next 2-3 months after the operation due to the complexity and mutually duplicated innervation and the possibility of regeneration of temporarily non-functional nerves and muscles.
If any temporary dysfunction occurs, we recommend the administration of vitamin B, E, D and patience till full recovery. Deformity of the lip can be camouflaged with botox administration to the uninjured side, which temporarily eliminates the function of the opposite depressor muscle.
Healing and recovery
Immediately after the operation, you will have little pain (no tension!). Nothing too excessive really. The development of swelling will gradually begin usually from the third day and there may be larger or smaller bruises. If drains are used, they will be taken out the next day. The role of drains is to prevent fluid accumulation and better adherence of skin at the dissected areas. The swelling is most pronounced about a week after the operation and then gradually subsides. Maximum swelling and also hardening of tissues often occurs in the area under the chin. This is related to the disruption of the lymphatic drainage of the area and disappears within up to 3 months of the operation.
You can take a shower already 24 hours after the operation.
For a period of at least 7 days, I recommend a resting regimen with restriction of bending and lifting of the head. I recommend a rather soft diet (detailed instructions of the diet, especially if gland trimming was done, can be found here), avoiding excessive opening of the mouth – these are instructions to avoid tearing the fixation of the deep layer. You may feel a strong pull in the area under the chin and on the neck or more difficult swallowing. After a week, it is already possible to use light make-up. It is necessary to limit sport activities for a period of up to 6 weeks. We minimize the compressive head band after the facelift to just for the first few days. It’s more of a nuisance than a help with the swelling. The swelling must subside by its own circulation through the lymphatic channels. The compression could suppress this even more. Lymphatic massages performed by a physiotherapist are wellcome. Since facelifts are ischemic interventions, hyperbaric oxygen therapy can help to improve healing after any such surgery, as Dr Jacono from New York demonstrated in his study (2). This treatment may be available at commercial establishments near where you live.
Deep plane face and necklift price
The final price of the surgery is influenced by its complexity and duration of surgery. The price is calculated after the consultation with the doctor.
Usual optional additional procedures in combination with a deep plane procedure:
- deep plane facelift
- deep plane necklift
- fatgrafting and nanofatgrafting
- correction of ear lobe
- submandibular salivary gland trimming
- upper and lower blepharoplasty
- direct or endo browlift
References:
1) Mendelson BC, Tutino R. Submandibular Gland Reduction in Aesthetic Surgery of the Neck: Review of 112 Consecutive Cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015 Sep;136(3):463-471. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000001526. PMID: 25989302; PMCID: PMC4548544.
2) Stong BC, Jacono AA. Effect of perioperative hyperbaric oxygen on bruising in face-lifts. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2010 Sep-Oct;12(5):356-8. doi: 10.1001/archfacial.2010.66. PMID: 20855782.
3) Tonnard P, Verpaele A, Peeters G, Hamdi M, Cornelissen M, Declercq H. Nanofat grafting: basic research and clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013 Oct;132(4):1017-1026. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e31829fe1b0. PMID: 23783059.
4) Talei B, Ziai H. PHAT Lips and PHAT Face: Platelet Hybridized Adipose Therapy for Superficial Musculoaponeurotic System and Dermal Rejuvenation. Facial Plast Surg. 2023 Nov 20. doi: 10.1055/a-2188-8608. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37816491.
5) Tonnard P, Verpaele A, Carvas M. Fat Grafting for Facial Rejuvenation with Nanofat Grafts. Clin Plast Surg. 2020 Jan;47(1):53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.cps.2019.08.006. Epub 2019 Oct 28. PMID: 31739897.
6) Semra Uyulmaz, Nadia Sanchez Macedo, Farid Rezaeian, Pietro Giovanoli, Nicole Lindenblatt, Nanofat Grafting for Scar Treatment and Skin Quality Improvement, Aesthetic Surgery Journal, Volume 38, Issue 4, April 2018, Pages 421–428.
7) Jacono AA, Alemi AS, Russell JL. A Meta-Analysis of Complication Rates Among Different SMAS Facelift Techniques. Aesthet Surg J. 2019 Aug 22;39(9):927-942. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjz045. PMID: 30768122.
Quick info
Anesthesia: general
Make-up: after a week
Sport: after 4 to 6 weeks
Hospitalization: 1 to 2 days
Back to normal life: after 2 to 3 weeks
Before & After Photos
Patient Reviews
Arrange a date for your consultation
Please contact us via form bellow or by phone.
+420 224 284 421 / +420 776 553 244
treatments
ADDRESS
MUDr. Radek Lhotsky
Formé Clinic
Jeseniova 30
130 00 Prague 3, Czech Republic